Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-08-19 Origin: Site
A collagen wound dressing helps your body heal wounds faster. It also makes healing more comfortable. You put it right on the wound. It forms a soft layer that helps the wound heal. Clinical studies show collagen dressings help wounds heal quicker. They also lower pain and cut down the chance of infection. These dressings work better than regular ones. For example, people using collagen dressings had wounds close faster. They also felt less pain when changing the dressing.
Collagen wound dressings help wounds heal faster. They keep wounds moist. They help new tissue grow. These dressings can make pain less. They also lower the chance of infection. This is better than regular bandages. Collagen dressings are made in sheets, gels, and pads. Each type fits different wounds and needs. They work best for chronic wounds, burns, and surgical wounds. They also help wounds with a lot of fluid. Always check if you have allergies. Follow your doctor’s advice to use collagen dressings safely. This helps you use them the right way.
Collagen is a special protein that your body uses to build strong skin and tissues. You find it in your skin, bones, tendons, and even in your blood vessels. It acts like glue, holding everything together and giving your skin its stretch and strength. When you get a cut or scrape, collagen helps repair the damage and makes new skin grow.
Collagen is made from amino acids like proline, glycine, and hydroxyproline.
These amino acids twist together to form a triple helix, which gives collagen its strength.
Type I collagen is the most common type in your body. It builds skin, bones, tendons, and ligaments.
Collagen supports fibroblast cells in your skin. These cells help make new tissue and replace old or damaged skin.
It also protects organs and helps your blood clot when you get hurt.
If your body does not have enough collagen, your skin can become weak or stretchy. Some people have diseases that affect collagen, like Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. This shows how important collagen is for keeping your skin and tissues healthy.
Tip: Collagen is not just for beauty. It plays a big role in wound repair and keeping your body strong.
You can find collagen dressings in many shapes and sizes. Each type works best for different wounds. Here are the most common forms you might see:
Sheets: Flat pieces that cover larger wounds.
Pads: Thicker dressings for wounds with more fluid.
Gels: Soft and easy to spread, good for deep or uneven wounds.
Sponges: Absorbent and flexible, great for wounds that need extra moisture.
Particles: Small bits that fill in gaps or holes in the wound.
Films: Thin layers that protect the wound surface.
Collagen wound dressing comes from several sources. Most dressings use animal collagen because it is similar to what you have in your body. Here are the main sources:
Bovine (cow): The most common source. It is strong and works well for most wounds.
Porcine (pig): Another popular choice. It is safe and does not carry the risk of prion diseases found in cows.
Equine (horse): Used in some dressings, especially in Europe.
Ovine (sheep) and Avian (bird): Less common, but still used in some products.
Bullfrog skin: A new, eco-friendly source that some companies use.
Lab-grown human collagen: Made in labs for people who want a non-animal option.
Form | Best For | Common Source |
|---|---|---|
Sheet | Large, flat wounds | Bovine, Porcine |
Pad | Wounds with heavy exudate | Bovine, Porcine |
Gel | Deep or irregular wounds | Bovine, Porcine |
Sponge | Moisture control | Bovine, Porcine |
Particle | Filling wound cavities | Bovine, Porcine |
Film | Surface protection | Bovine, Porcine |
You might wonder if there is a difference between bovine and porcine collagen. Both types work well and help wounds heal. They both support cell growth and tissue repair. Porcine collagen is a good choice if you worry about diseases linked to cows. Both types are safe and have a long history in medicine.
Note: Some dressings mix collagen with other things like silver or hyaluronic acid. These extras can help fight infection or speed up healing.
When you use a collagen wound dressing, you give your wound a boost. Collagen dressings do more than just cover the wound. They help your body heal in several ways:
Collagen dressings create a moist environment. This helps cells move and grow faster. Dry wounds heal slower because scabs block new cells from moving in.
The dressing acts like a scaffold. It gives cells a place to stick and build new tissue. This is called the extracellular matrix.
Collagen attracts fibroblasts. These are special cells that make new collagen and help close the wound.
The dressing binds to harmful enzymes called matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Too many MMPs can break down healthy tissue. Collagen dressings protect the wound by soaking up these enzymes.
Collagen dressings help new blood vessels grow. This brings oxygen and nutrients to the wound, speeding up healing.
They also keep growth factors and proteins in the wound longer. This helps the skin repair itself faster.
Here is a quick list of what collagen dressings do for your wound:
Keep the wound moist and comfortable
Support new tissue growth
Attract healing cells like fibroblasts and keratinocytes
Block harmful enzymes that slow healing
Help blood vessels form in the new tissue
Reduce swelling and inflammation
Studies show that wounds treated with collagen dressings heal faster than those with dry dressings. Moisture helps more fibroblasts grow, which means more new tissue. The dressing also helps remove dead tissue and lowers the risk of infection.
Collagen wound dressing is a smart choice for many types of wounds. It works with your body, not against it. You get a cleaner, safer, and faster healing process.
Collagen dressings help your wound heal from inside. They do more than just cover the wound. These dressings help your body’s cells go where they need to. Here is what happens:
Collagen dressings help healing cells move to the wound. Your body sends fibroblasts and macrophages to help.
Fibroblasts start making new collagen. This helps new tissue grow and close the wound.
Collagen dressings act like a scaffold. Cells stick to them and fill in the wound.
The dressings guide fibroblasts to the wound. This makes healing faster.
Collagen dressings help organize new collagen fibers. This makes new tissue strong and flexible.
They lower elastase levels. Elastase can slow healing in wounds that last a long time.
Collagen dressings change the wound’s chemistry. They fix problems so your wound heals better.
Did you know? Collagen, especially Type I, works with cells like keratinocytes and endothelial cells. These cells help make new skin and blood vessels. Both are important for wound healing.
When you put on a collagen dressing, you help granulation tissue form. Granulation tissue is pink and bumpy. It fills the wound as it heals. Collagen dressings soak up harmful enzymes called MMPs. Too many MMPs can hurt healthy tissue and slow healing. By soaking up these enzymes, collagen dressings help your wound heal faster.
Studies show using pure native collagen dressings early helps the wound bed. This makes it easier for your body to use other treatments, like skin grafts. Collagen dressings also keep the wound moist. This helps new collagen fibers and granulation tissue grow.
Here is a quick look at what collagen dressings do:
Step in Healing Process | What Collagen Dressings Do |
|---|---|
Cellular Migration | Attract fibroblasts and macrophages |
Collagen Deposition | Guide new collagen fibers into the wound |
Granulation Tissue Formation | Support new blood vessels and tissue growth |
Enzyme Regulation | Absorb MMPs and reduce elastase |
Biochemical Balance | Correct imbalances in chronic wounds |
Collagen dressings give your wound the best chance to heal. They help your body build strong tissue and move past slow healing.
Keeping the right moisture in your wound is important. Collagen dressings help by soaking up extra fluid called exudate. They also keep the wound moist. This balance helps your wound heal.
Collagen dressings soak up moderate to heavy exudate. They form a gel-like layer over the wound. This gel keeps the wound moist. Moist wounds heal faster and feel better.
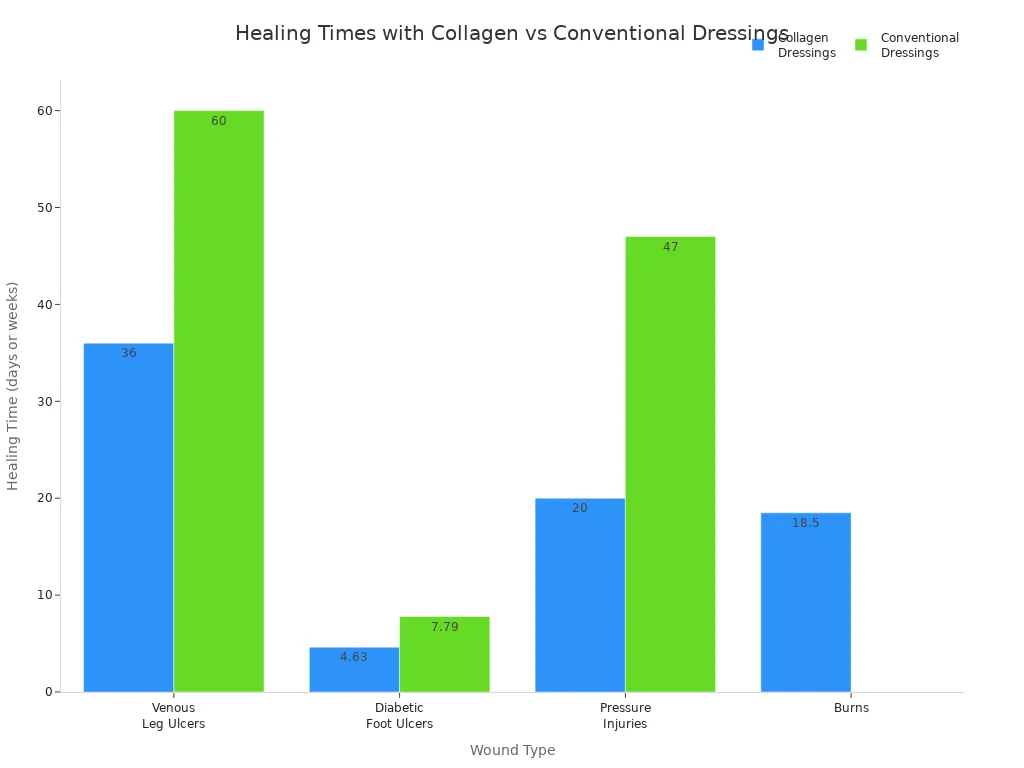
You can use collagen dressings on many wounds. These include diabetic foot ulcers, venous leg ulcers, pressure ulcers, burns, surgical wounds, and traumatic wounds. The dressings come in sheets or powders. You can pick the best one for your wound’s shape and fluid amount.
Collagen dressings do more than soak up fluid. They act as sacrificial substrates for MMPs. This means the enzymes attack the dressing, not your healthy tissue. By binding and lowering these enzymes, collagen dressings help your wound heal faster.
Some collagen dressings mix in other materials. These include ORC, alginate, or carboxymethylcellulose. These extras help absorb exudate and keep the wound moist. Some dressings add silver to fight infection. You usually cover the collagen dressing with another dressing. This keeps it in place and manages extra fluid.
Tip: A moist wound helps stop scabs and lets new cells move in fast. This means less pain and quicker healing.
Collagen dressings help you control moisture and exudate. They protect your wound from getting too wet or too dry. This helps tissue repair and lowers swelling. Your wound stays in the best state for healing.
Protecting your wound from infection is very important. Collagen dressings help in many ways. Some advanced collagen dressings use hydrogels with antimicrobial peptides. These peptides attack bacteria by breaking their cell walls. This action lowers infection risk, even in wounds that last a long time.
Some dressings use PTT and PDT. These methods use light to kill bacteria and help the dressing work better. The hydrogels can also carry oxygen. This helps wounds that do not get enough air. More oxygen means better healing and stronger protection.
Recombinant type III collagen in some hydrogels helps tissue repair. It also helps new blood vessels grow. This protects against infection and helps wounds heal faster. The hydrogel dressings work quickly to remove bacteria and keep your wound safe. This is good for wounds that take longer to heal.
Note: Collagen dressings with silver or antimicrobial peptides give extra protection. They help keep your wound clean and lower infection risk while healing.
Collagen dressings do more than cover your wound. They fight bacteria, help new tissue grow, and keep your wound ready to heal. This makes collagen dressings a smart choice for anyone with a wound that needs extra care.
You want your wound to heal quickly and hurt less. Collagen dressings help you do this. These dressings make a moist layer on your wound. This layer stops the wound from getting dry. It helps new skin grow faster. You feel less pain because collagen dressings protect nerve endings. They also stop the wound from sticking to the bandage.
Clinical studies show collagen dressings heal wounds faster. People with herpes zoster wounds heal quicker and feel less pain.
Collagen dressings keep wounds moist. This helps new skin and blood vessels grow. It also helps your body make more collagen.
You have less chance of infection. The moist layer blocks germs and keeps your wound safe.
Many people need less pain medicine. Some stop taking oral painkillers because collagen dressings make them feel better.
Collagen dressings help your body make more fibroblasts and blood vessels. Your wound heals better and looks nicer when it closes.
Tip: Collagen dressings do more than cover wounds. They help your body heal inside and make you feel better while healing.
You can use collagen dressings for many wounds. They work for new wounds and wounds that last a long time. If you have a chronic wound, healing can be hard. Collagen dressings give your wound extra support.
Here are some wounds that do well with collagen dressings:
Chronic wounds like diabetic foot ulcers, pressure ulcers, and venous leg ulcers
Surgical wounds that need more support
Burns that need a moist place to heal
Traumatic wounds with tissue loss
Donor sites after skin grafts
Wounds with lots of fluid (exudate)
Collagen dressings help you take care of chronic wounds. They keep wounds moist and soak up extra fluid. They help new tissue grow. You can use them for slow-healing wounds or wounds that need more protection. If regular dressings do not help, collagen dressings may work better.
Note: Collagen dressings come in different forms. You can choose sheets, gels, or powders for your wound’s shape and size.
Some wounds should not use collagen dressings. Certain health problems make these dressings unsafe. You need to know when not to use them to keep your wound safe.
Contraindication / Patient Condition | Reason / Risk Description |
|---|---|
Exposed unprotected organs or vessels | Risk of organ and vessel damage, increased bleeding, fistula formation |
Inadequate or potential for inadequate wound hemostasis | Increased risk of bleeding |
Acutely ischemic wounds | Risk of necrosis due to reduced tissue perfusion |
Surgically closed incisions | Not recommended due to risk of damage and improper healing |
Hypersensitivity to dressing components | Potential allergic reactions causing nonhealing or worsening wounds |
Untreated osteomyelitis | Increased potential for spread of infection |
Untreated malignancy at wound site | Risk of promoting unwanted tissue growth and increased bleeding |
Unexplored fistulas | Risk of fistula eruption and damage to organs or vessels |
Third-degree burns | Risk of skin damage due to drape adhesion |
Patients with weakened or friable blood vessels or organs | Increased bleeding risk |
Patients on anticoagulants or platelet aggregation inhibitors | Increased bleeding risk |
Wounds with mixed vascular etiologies or bleeding surfaces | Not recommended due to bleeding risk |
If you have any of these problems, talk to your doctor first. Some wounds need special care. Using the wrong dressing can slow healing or cause harm.
Alert: Always check for allergies to collagen or other dressing materials. If you see redness, swelling, or pain, stop using the dressing and call your doctor.
To use collagen dressings, first clean your wound well. Follow the steps your nurse or doctor gave you. Put the collagen dressing right on the wound. Make sure the wound stays moist. Cover it with a non-stick layer like paraffin gauze or Telfa™. Add a layer of gauze on top to soak up fluid. Hold everything in place with a bandage.
Here is an easy guide:
Wash the wound as your care plan says.
Put the collagen dressing on the wound.
Place a non-stick layer over the dressing.
Add a layer that soaks up fluid.
Wrap a bandage around everything.
Change the dressing every 1 to 3 days, based on how wet the wound is.
Rinse off any leftover collagen when you change it.
If you use a sheet, wet the edges with saline so it sticks better.
For deep wounds, mix collagen particles with saline to make a paste.
Watch for too much tissue growing. If you see this, stop using collagen dressings and call your doctor.
Tip: Always look for signs of infection or too much tissue when you change the dressing.
You might wonder how collagen dressings are different from regular ones. Collagen dressings help your body heal by helping new tissue grow. They also keep the wound moist. Regular dressings, like plain gauze, just cover the wound and keep dirt out.
Feature | Collagen Dressings | Traditional Dressings |
|---|---|---|
Moisture Control | Keeps wound moist | Often dries out wound |
Healing Support | Promotes tissue growth | Offers little support |
Enzyme Regulation | Reduces harmful enzymes | No effect |
Comfort | Less pain on removal | Can stick and hurt |
Use for Chronic Wounds | Yes | Not as effective |
Collagen dressings are good for wounds that heal slowly. They give extra help to wounds that need it.
You need to be careful when using collagen dressings. Some people are allergic to animal products. If you know you are allergic to collagen or anything in the dressing, do not use it. If you see redness, swelling, or itching, stop using the dressing right away.
Safety Concern | Description | Example/Source |
|---|---|---|
Allergic Reactions | Allergies to marine or bovine collagen can cause serious reactions. | Reports of anaphylaxis and allergic cases in clinical use. |
Disease Transmission Risk | Bovine and porcine collagen may carry a small risk of disease transmission. | Concerns about BSE and prion diseases in medical products. |
Safer Alternatives | Marine collagen may be safer for some people. | Suggested for those worried about animal disease risks. |
Do not use collagen dressings if you are allergic to animal products.
If your dressing has silver, check if you are allergic to silver.
Always use these dressings with a doctor’s help, especially if you need compression therapy.
Note: If you have a wound that heals slowly or special health needs, talk to your doctor before using collagen dressings.
Collagen dressings help wounds heal faster and lower pain. They also lower the chance of infection. These dressings keep the wound moist and help new tissue grow. They help your body fight off bacteria. You can use collagen dressings for burns, chronic wounds, and after surgery. Collagen dressings work better than regular dressings for healing and comfort.
You should ask your doctor before using collagen dressings. Doctors help you pick the right dressing for your wound. They also check how your wound is healing. Good choices in wound care help you heal faster and feel better.
You get more than just coverage. Collagen dressings help your skin grow new tissue. They keep the area moist. Regular bandages only protect the surface. Collagen dressings support healing inside the wound.
Yes, you can use them at home. Always follow your doctor’s instructions. Clean the wound first. Place the dressing as directed. Change it as often as your care plan says. Watch for signs of infection.
Most collagen dressings stay on for one to three days. Your doctor may tell you to change it sooner if the wound gets wet or dirty. Always check the dressing and follow your care plan.
Most people can use them safely. Some people have allergies to animal products. If you notice redness, swelling, or itching, stop using the dressing. Talk to your doctor before starting any new wound care product.
Chronic wounds, burns, surgical wounds, and ulcers heal well with collagen dressings. These dressings help when healing takes longer. They work best for wounds that need extra support to grow new tissue.
Foshan Facility
Guangdong Victory Biotech Co., Ltd.
Address: 4F., A11, Guangdong New Light Source Ind00ustrial Park, Luocun, Shishan Town, Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province, 528226, China.
Tel: +0757 8561 9788
Mobile: +86 18138941037
Email: service@victorybio.com
Wuzhou Facility
Wuzhou Victory Biotech Co., Ltd.
Address: Building 29, No. 30, 31, Fudian Shangchong, Xijiang Fourth Rd., Wuzhou City, Guangxi Province, China.
